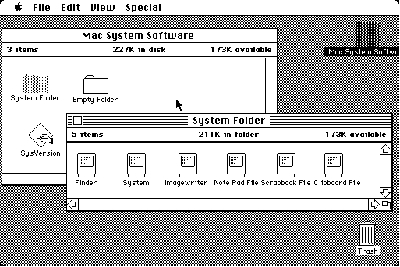
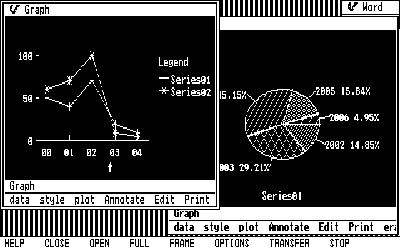
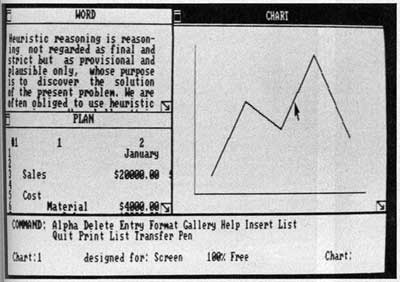
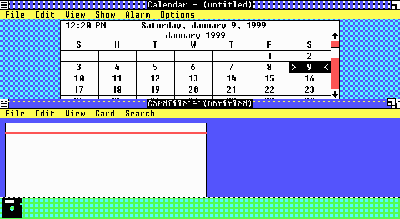
Introduction
Today, almost everybody in the developed world interacts with personal computers in some form or another. We use them at home and at work, for entertainment, information, and as tools to leverage our knowledge and intelligence. It is pretty much assumed whenever anyone sits down to use a personal computer that it will operate with a graphical user interface. We expect to interact with it primarily using a mouse, launch programs by clicking on icons, and manipulate various windows on the screen using graphical controls. But this was not always the case. Why did computers come to adopt the GUI as their primary mode of interaction, and how did the GUI evolve to be the way it is today?
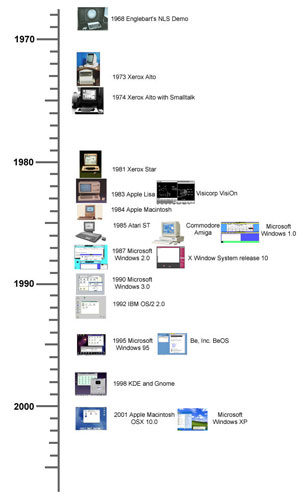
In what follows, I?ll be presenting a brief introduction to the history of the GUI. The topic, as you might expect, is broad, and very deep. This article will touch on the high points, while giving an overview of GUI development.
Prehistory
Like many developments in the history of computing, some of the ideas for a GUI computer were thought of long before the technology was even available to build such a machine. One of the first people to express these ideas was Vannevar Bush. In the early 1930s he first wrote of a device he called the "Memex," which he envisioned as looking like a desk with two touch screen graphical displays, a keyboard, and a scanner attached to it. It would allow the user to access all human knowledge using connections very similar to how hyperlinks work. At this point, the digital computer had not been invented, so there was no way for such a device to actually work, and Bush's ideas were not widely read or discussed at that time.